SPINNING AND ITS CLASSIFICATION
SPINNING:-
The process of making yarn from fibres is called spinning. In this process fibres from a mass of cotton wool are drawn out and twisted. By this fibres come together to form a yarn. Spinning can be done by hand, by takli and charkha.
Spinning, in textiles, process of drawing out fibres from a mass and twisting them together to form a continuous thread or yarn.
Spinning is the process of drawing out and twisting fibres to join them firmly together.
The process of making fibrous material into yarn or thread. The act of process of twisting fibers as cotton or rayon, into yarn or thread. The extraction of a fiber forming solution through a spinner to form filament.
CLASSIFICATION OF SPINNING:-
- CHEMICAL SPINNING:-
Melt spinning is a metal forming technique that is typically used to form thin ribbons of metal or alloys with a particular atomic structure. ... A typical melt spinning process involves casting molten metal by jetting it onto a rotating wheel or drum, which is cooled internally, usually by water or liquid nitrogen.
Example,
polyster, nylon, polypropylene etc.
SPECIAL FEATURES OF MELT SPINNING:
high production
hazard, non toxic
no environment pollution
high heat
MELT SPINNING FLOW DIAGRAM:-
MANUFACTURING PROCESS:-
In this technique, the common man-made fibers spun are nylon, polypropylene, etc.
First the fiber forming polymer chips are fed through a hopper into a spinning vessel.
In spinning vessel, melts by the heated grid and passes through the grid mesh and collected on the pool.
Then the melt is metered by a pump through a filter and finally through the spinneret.
The melt solidifies immediately it issues from the jets and so form filaments passes through a cooling chamber in which cold air current swept across the filaments.
The spinning speed is 1000-2000 m/min.
ADVANTAGES:-
The melting process is very simple.
Any production rate can be achieved.
It avoids the need for a solvent recovery plant and loss of solvent during recovery.
High speed of production.
No purification problems.
Easy to get required cross section.
DISADVANTAGES:-
Separate drawing steps.
2. MECHANICAL SPINNING:-
WET SPINNING
Wet spinning is the oldest of the four spinning process. The process is used for polymer that need to be dissolved in a solvent to be spun. The spinneret is submerged in a chemical bath that causes the fiber to participate and the solidifs, as it emerges. This process gets its name from this “wet bath”
Example,
Acrylic, viscose rayon, aramid, modaecrylic, spamdex, etc.
SPECIFIC FEATURES OF WET SPINNING:-
Required solvent
Chemical and wet bath may be used.
Low production (speed 70-150 yards/min)
WET SPINNING FLOW DIAGRAM:-
MANUFACTURING PROCESS:-
In this method, the common man-made fibers like acrylic, viscose rayon, aramid, modacrylic, spandex, are produced.
First, the fiber forming polymer solution is prepared.
Then the solution is pumped under a particular pressure through the metering pump.
Then the solution is passed through the filter.
Finally the polymer solution is passed through the spinneret.
The spinneret are immersed in a spin bath containing coagulating the bath.
It becomes coagulated by the chemicals of the spin bath.
The rate of the solution feeding and rate of holes per spinneret may be 1,00,000 nnumber/square inch diameter and the space of holes in the sppinneret could be varied.
ADVANTAGES:-
Large tows can be handled.
Produce quality yarns.
DISADVANTAGES:-
Low production rate(speed 70-150 yards/min)
Additional washing, drying proocess are involved.
This process is very long and it's a continuous process.
Solvent and chemical recovery.
It is difficult to get required cross section.
DRY SPINNING
Dry spinning is the third spinning used in textile industry. Fibers produced by these spinning techniques are acetate rayon and acrylic fibers.
SPECIAL FEATURES OF WET SPINNING:-
Dry (warm) air
Speed 70-150 yards/min
Elammable solvent hazards
TYPICAL DRY SPUN FIBERS:-
Acetate (acetone solvent)
Triacetate (methylene chloride)
Spandex (dimethyl formamide)
DRY SPINNING FLOW DIAGRAM:-
MANUFACTURING PROCESS:-
First the fiber forming materials are dissolved in volatile solvent.
Each spinning unit consists of a pump and spinneret at the top above 9 to 20 feet high.
There is an air outlet at the top of the tall shift and air inklet at the bottom.
Then the fiber spinning solution is forced under pressure from the storage tank to the spinning pump.
Then it passed through the spinneret.
The number of holes, diameter of the holes and shape of the holed varies.
The fineness of the filament is determined by the diameter of the holes.
Primarily by the relation between the rate at which solution is forced through the spinneret.
The rate at which the yarn is wind up.
Next the spinning solution emerging from the spinnertet meet the warm air, volatile solvent evaporates leaving the filaments.
Hence, coagulation takes place and becomes dried before leaving the chamber.
ADVANTAGES:-
Large tos can be handled.
Preparation of solvent is easy.
Yarn does not required purification.
DISADVANTAGES:-
Flammable solvent hazards.
Solvent recovery
Slow process (200-400 yards/min)
If the solvent used is volatile some precaution should be taken.
Solvent should be easily evaporated.
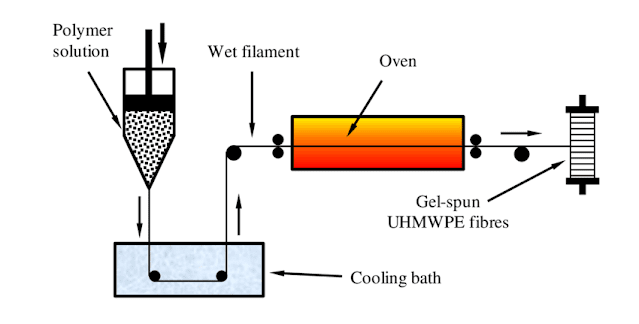
GEL SPINNING
Gel spinning is otherwise called as dry-wet spinning. This type of spinning is commonly used for high strength or other special properties of fibers. Here the polymer is used in gel form.
GEL SPINNING FLOW DIAGRAM:-
MANUFACTURING PROCESS:-
The filaments first pass through air and then cooled in a liquid bath
Gel spinning is commonly produced strong fibers and the fibers having special properties.
The polymer is partially in liquid or in gel form.
It keeps the polymer chains somewhat bound together at various points in liquid crystal form.
The strong inter-chain forces in the fiber increasing its tensile strength.
The polymer chains with in the fibers also have a large degree of orientation, which increases its strength.
The filament comes out with an enchancing strength.
The high strength polypropylene fiber and amide fibers are manufactured by using of this process.
ADVANTAGES:-
Increase tensile strength.
The fiber is very strong.
High performance fiber can produce.
DISADVANTAGEs:-
Solvent easily evaporated.
Low production.







Comments
Post a Comment